α degrees α radians 180 π. This Trigonometry Calculator uses RAD mode or radian mode.

Reference Angle Calculator Definition Graph Quadrants
Pi radians are equal to 180 degrees.
Reference angle calculator radians. 1 π180 0005555556π 001745329252 rad. 180π radians From above we have 1 radian 180π 0. Radian Measure and Circular Functions.
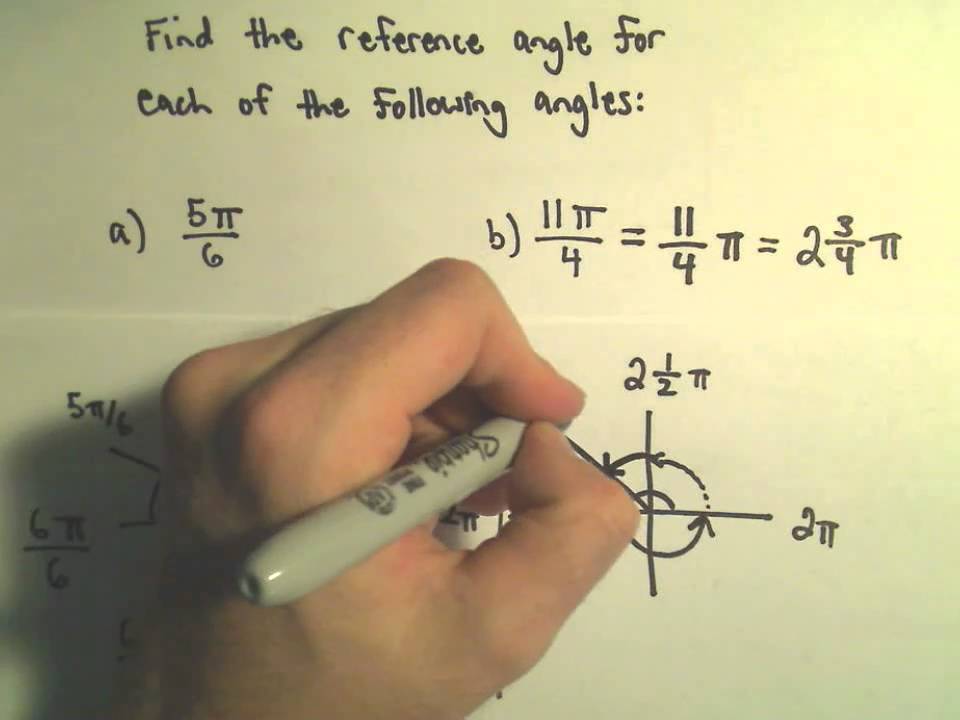
Remember that they are not the same thing - the reference angle is the angle between the terminal side of the angle and the x-axis and its always in the range of 0 90 or 0 π2. Find an angle that is positive less than 2π 2 π and coterminal with 19π 6 19 π 6. The thing which can sometimes be confusing is the difference between the reference angle and coterminal angles definitions.
It explains how to find the reference angle in radians and degrees. This trigonometry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into reference angles. 360 degrees is equal to 628319 radians Conversion Table.
Complementary angle calculator that returns exact values and steps given either one degree or radian value Trigonometry Calculator. Coterminal Angle Definition A coterminal angle is an angle that ends at the same geometric point on the coordinate plan as another angle. Convert 360 degrees to radians show work Formula.
360 degrees x π180 628319 radians Result. 10π9 is a bit more than π so it lies in the third quadrant. The radian is the SI derived unit for angle in the metric system.
Tap for more steps. Pi radians are equal to 180 degrees. Solving for the reference angle in radians is much easier than trying to determine a trig function for the original angle.
Input your angle data to find the reference angle reference angle 80 How to Find a Reference Angle in Radians Finding your reference angle in radians is similar to identifying it in degrees. For example 1 radian can be written as 1 rad 1 c 1 r or 1 R. Use of the coterminal angle calculator 1 - Enter the angle.
This article explains what a reference angle is providing a reference angle definition. π rad 180. Click DEG to change Degree Mode.
Find the Reference Angle. It is used instead of degrees. The angle made at the center of a circle by an arc whose length is equal to the radius of the circle is equal to One radian.
If your angle is larger than 2π take away the multiples of 2π until you get a value thats smaller than the full angle. To convert degrees to radians take the number of degrees to be converted and multiply it by π180. Reference Angle Calculator Enter the original angle into the calculator to evaluate the reference angle.
1 rad 180π 57295779513 The angle α in degrees is equal to the angle α in radians times 180 degrees divided by pi constant. Example 745 in Radians second input. When you want to recalculate angles into their acute version then a reference angle calculator can be the best tool to have.
Subtract 2 π 2 π from 19 π 6 19 π 6. This used for trigonometric calculation. π rad 180 One radian is equal 57295779513 degrees.
So if our given angle is 214 then its reference angle is 214 180 34. Use of Reference Angle and Quadrant Calculator 1 - Enter the angle. Radians are often expressed using their definition.
How to use Trigonometry Calculator. There are about 628318 radians in a circle. When the terminal side is in the third quadrant angles from 180 to 270 our reference angle is our given angle minus 180.
For example to convert 120 degrees you would have 120 x π180 120π180. 001745 radians in a degree. α radians α degrees π 180.
To compute the measure in radians of the reference angle for any given angle theta use the rules in the following table. 1 radian 573R degrees. One degree is equal 001745329252 radians.
Example 745 in Radians input enter angle as a fraction of π. Radian Radian is a unit for angles measure. Example 125 π then press the button Calculate on the same row.
If you enter a quadrantal angles such as 90 -180 0 the message This is a quadrantal angle will be displayed. For this example well use 28π9 2. Finding Reference Angles in Radians Quadrant Measure of Angle Theta Measure of.
Since the coordinate circle has as a total rotation of 360 degrees adding or subtracting that to the angle yields a result as does the coterminal angle calculator above. Degrees to radians converter How to convert radians to degrees. In this example the reference angle is reference angle angle - π π9.
π2 to π - second quadrant so reference angle π - angle π to 3π2 - third quadrant so reference angle angle - π 3π2 to 2π - fourth quadrant so reference angle 2π - angle. Alternatively if the angle is unknown but the lengths of the two sides of a right angle triangle are known calculating the cotangent is just a matter of dividing the adjacent by the opposite side. Once youve gotten your answer simplify the radians.
Degrees The degree is a measurement unit of angles. Since there are an infinite number of coterminal angles this calculator finds the one whose size is between 0 and 360 degrees or between 0 and 2π depending on the unit of the given angle. Our cotangent calculator accepts input in degrees or radians so once you have your angle measurement just type it in and press calculate.
19 π 6 2 π 19 π 6 - 2 π. Degrees x π180 radians Calculations. The angle α in radians is equal to the angle α in degrees times pi constant divided by 180 degrees.
19π 6 19 π 6. Radians can be abbreviated as rad and are also sometimes abbreviated as c r or R. In Degrees top input.
You can calculate this by converting both numbers into fractions. For example cos 1 the same as cos 1 RadSome calculators use RAD Mode or Radian 1 RAD 57296 as a standard-setting.
And then this angle which is considered to be an exterior angle. For a square the exterior angle is 90.
Exterior Angles Of Polygons Examples Solutions Videos Worksheets Activities
For example if the measurement of the exterior angle is 60 degrees then dividing 360 by 60 yields 6.
How do you find the measure of an exterior angle. If two points are given then exactly one line can be drawn through those two points. The exterior angles taken one at each vertex always sum up to 360. For example the interior angle is 30 we extend this side out creating an exterior angle and we find the measure of the angle by subtracting 180 -30 150.
Find the measure of the exterior angle. Sine cosine and tangent are used to calculate angles and lengths in right-angled triangles. Exterior angles of polygons.
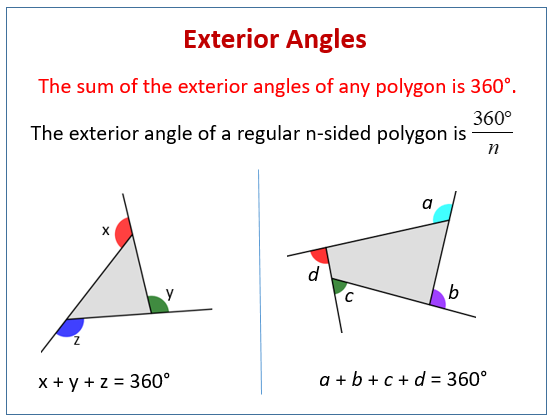
The measure of each interior angle of an equiangular n -gon is If you count one exterior angle at each vertex the sum of the measures of the exterior angles of a polygon is always 360. An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the opposite interior angles. Exterior angles of a triangle - Triangle exterior angle theorem.
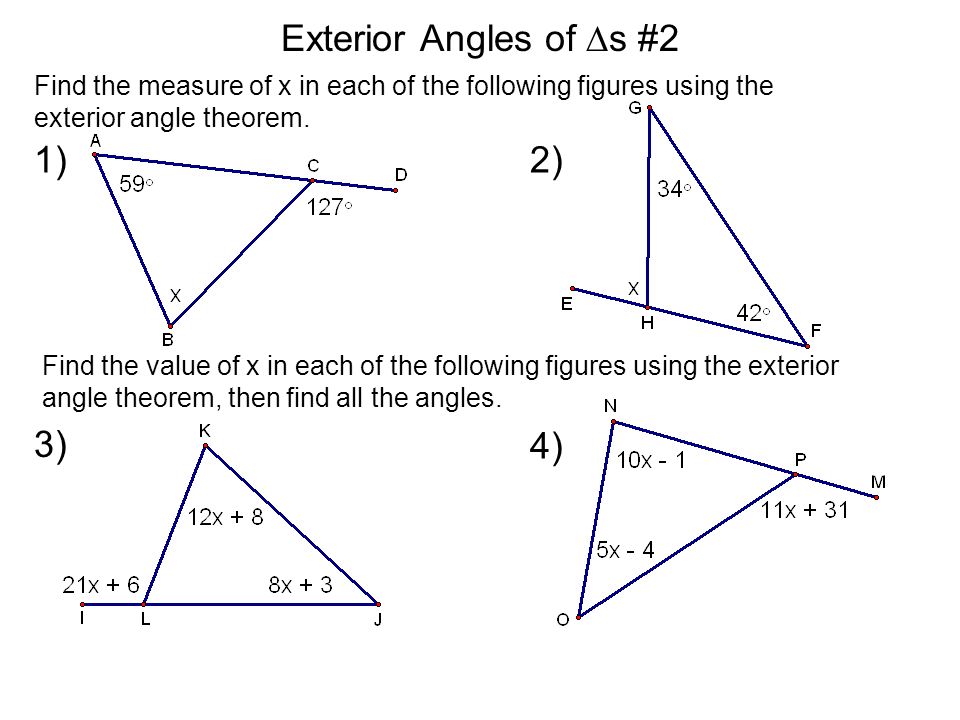
Since the interior and exterior angle together add up to a straight line their values should equal 180 degrees. Fr t is a vector field at the spatial position r at time t Σ is a surface bounded by the closed curve Σ dA is a vector element of the surface Σ ds is a vector element of the curve Σ v is the velocity of movement. If the measure of the exterior angle is 3x - 10 degrees and the measure of the two remote interior angles are 25 degrees and x 15 degrees find x.
The sum of the exterior angles of a polygon is 360. If you already have the other exterior angle measurements you can use those to help you find your missing measurements. The sine and cosine rules calculate lengths and angles in any triangle.
Try this with a square then with some interesting polygon you invent yourself. If you prefer a formula subtract the interior angle from 180. The answer is 200 square inches.
Work out 10 x 10 results 100 square inches then work out 100 x 2 200. The exterior angle d is greater than angle a or angle b. The measure of an exterior angle our w of a triangle equals to the sum of the measures of the two remote interior angles our x and y of the triangle.
So in this example y is an exterior angle. If I have lets say that these 2 angles-- lets say that the measure of that angle is a the measure of that angle is b the measure of this angle we know is going to be 180 minus a minus b. Every triangle has six exterior angles two at each vertex are equal in measure.
Which geometry term does the statement represent. Remember the sum of the exterior angles of ANY polygon is always 360 degrees. First you have to create the exterior angle by extending one side of the triangle.
For our equilateral triangle the exterior angle of any vertex is 120. Together the adjacent interior and exterior angles will add to 180. Looking for the missing measurements of exterior angles in a polygon.
A Polygon is any flat shape with straight sides. Six is the number of sides that the polygon has. Mathematics 21062019 1450 kaylonjohnwell23.
The three trigonometric ratios. Thats this angle right over here. Use The Law of Sines to solve for each of the other two sides.
Calculate c â a² b² - â Finding Unknown Angle Measures Answer Key - Displaying top 8 worksheets found for this concept. Next the measure is supplementary to the interior angle. A Leibniz integral rule for a two dimensional surface moving in three dimensional space is where.
Finding an Angle in. The Exterior Angles of a Polygon add up to 360. The exterior angle d equals the angles a plus b.
Interior and exterior angle formulas. Lets try two example problems. Therefore we have a 150 degree exterior angle.
Need help with how to find the missing angle of a triangle step by step. All you have to do is set up and solve an equation where the expressions are congruent. 1 Get Other questions on the subject.
Brought to you by Sciencing Divide 360 by the amount of the exterior angle to also find the number of sides of the polygon. Find the measure of the exterior angle. In other words the exterior angles add up to one full revolution.
Press Play button to see. The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon with n sides is n 2180. Using our new formula any angle n 2 180 n For a triangle 3 sides 3 2 180 3 1 180 3 180 3 60.
If the side of a polygon is extended the angle formed outside the polygon is the exterior angle. To find the measurement of an exterior angle simply take the corresponding interior angle and subtract it from 180. Multiply the length by the height and then double the product.
So our new formula for finding the measure of an angle in a regular polygon is consistent with the rules for angles of triangles that we have known from past lessons. Multiply length by height.