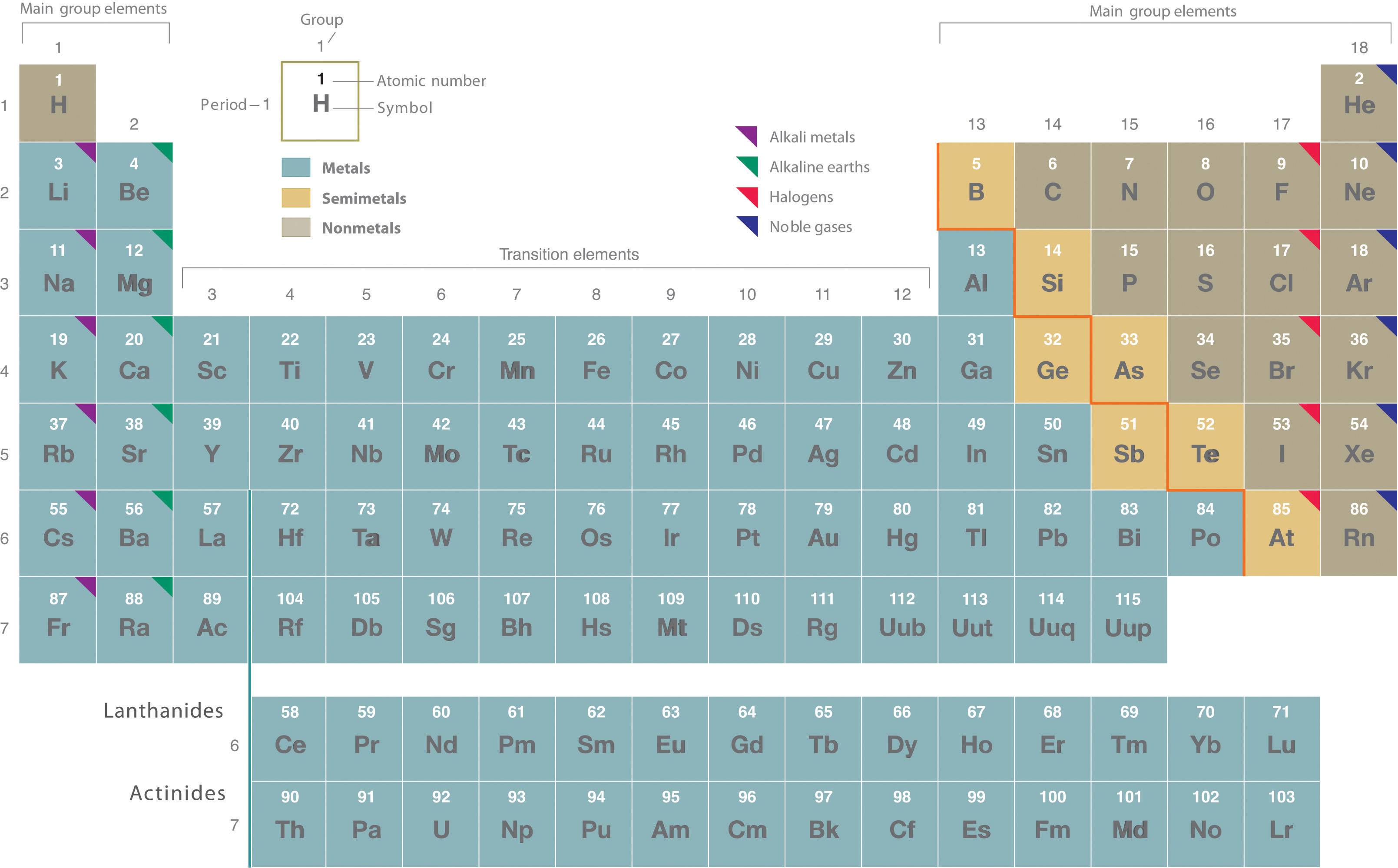
The periodic table presents all the elements known so far which are organized and located according to their characteristics and relationship between them in group periods blocks and metals metalloids and non-metals. 1 This group of elements is made up of all different states of matter solid liquid and gas a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 2 These elements always have a shiny luster a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 3 These elements are located in a stair step pattern on the periodic table a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 4 Elements in this group are good conductors of heat AND electricity a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 5 This tells you.

Printable Periodic Tables Science Notes And Projects Science Notes Periodic Table Periodic Table Of The Elements
One useful way is by metals nonmetals and metalloids.
Periodic table groups metals nonmetals metalloids. Most elements are metals. High density High strength Resistance to corrosion The SHOULD be up in the regular table but they simply would not fit without messing up the make-up of the table as we have it. The IUPAC definition defines a transition metal as an element whose atom has a partially filled d sub-shell or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell.
These elements are called metalloids. Metalloids Some elements between the metals and non-metals in the periodic table have properties which are a mixture of the properties of metals and non-metals. Metals left side of a period generally have a lower electron affinity than nonmetals right side of a period with the exception of the noble gases.
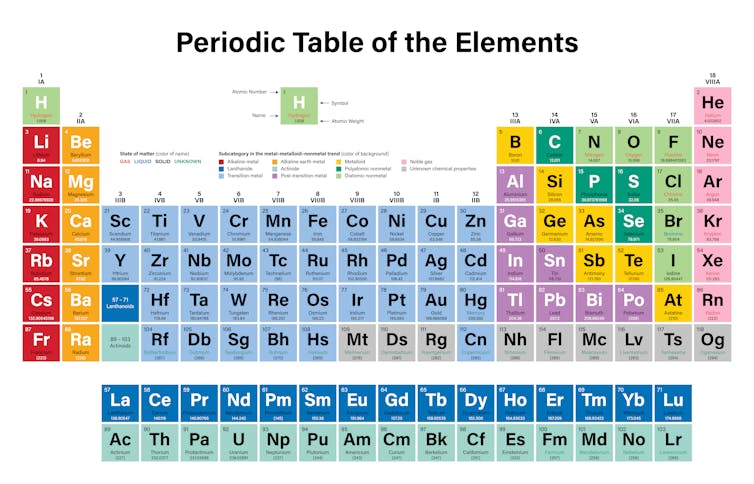
Periodic table groups metals nonmetals metalloids periodic table groups transition metals periodic. Metals Nonmetals Metalloids The periodic table on the left separates elements into three groups. The periodic table is made up of 18 groups of elements organized in vertical columns numbered from 1 to 18 from left.
Elements of the periodic table are grouped as metals metalloids or semimetals and nonmetals. Periodic Table Of The Elements Metals. Best Of Periodic Table Groups Metals Metalloids And Nonmetals.
It is designed to be used in conjunction with a notes packet for. The metalloids also known as semi-metals are placed between metals and non-metals in the periodic table of elements. Search Help in Finding Periodic Table Metals NonMetals and Metalloids - Online Quiz Version Periodic Table Metals NonMetals and Metalloids online quiz.
The Position Of The Inner Transition Elements Is Toppr Com. This is an online quiz called Periodic Table Metals NonMetals and Metalloids There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. Metals Nonmetals Metalloids - Maze chase.
The noble gases are almost completely inert. The periodic table is organized in families and periods. The metals green in the table nonmetals orange and metalloids blue.
The reactive nonmetals near the metalloids show some incipient metallic character such as the metallic appearance of graphite black phosphorus selenium and iodine. Also many periodic tables have a stair-step line on the table identifying the element groups. In chemistry the term transition metal or transition element has three possible definitions.
They are found in a stair step line that helps differentiate metals from non-metals in this element table. Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Using the periodic table you can classify the elements in many ways. According to their shared physical and chemical properties the elements can be classified into the major categories of metals metalloids and nonmetals.
This is a brief overview of how the periodic table is divided into three major groups called Metals Non-metals and Metalloids. Shiny Ductile Good Conductor Poor insulators Located on the Left side of the periodic table Mallable Metalloids. Metalloids-Metalloids are the group of certain elements which has both the.
Examples of non-metals are carbon nitrogen etc. Non-Metals are present on the right side of the periodic table. Metallic properties decrease as we move from left to right across the groups.
They are usually shiny very dense and only melt at high temperatures. Shiny or dull Brittle or malleable Semi-Conductors Staircase on the Periodic Table Non-metals. Look at Image Dull Brittle Poor Conductors Good Insulators Located on the right side Not Ductile.
The metalloids separate the metals and nonmetals on a periodic table. There are seven elements that are classified as metalloids and placed in Group 13 14 15 16 and 17. Z e e s These are still metals and they share the same patterns as all of the other metals in the table.
These elements are distinctive in that they typically have low melting and boiling points dont conduct heat or electricity very well and tend to have high ionization energies and electronegativity values. Properties of these series. From left to right in the periodic table the nonmetals can be divided into the reactive nonmetals and the noble gases.
The line begins at boron B and extends down to polonium Po. Many scientists describe a transition metal as any element in the d-block of the periodic table which includes groups. The nonmetals or non-metals are a group of elements located on the right side of the periodic table except for hydrogen which is on the top left.
The metalloids separate the metals and nonmetals on a periodic table. Also we can say that metalloids are present in the diagonal region of the p block on Periodic table.
Groups And Periods Of The Periodic Table Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids Elements And The Periodic Table
Periodic Table of the Elements Mg meta loids.

Periodic table showing metals nonmetals and metalloids. Metalloids have properties of both metals and non-metals. Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Using the periodic table you can classify the elements in many ways. Properties of Metals Nonmetals Metalloids Created Date.
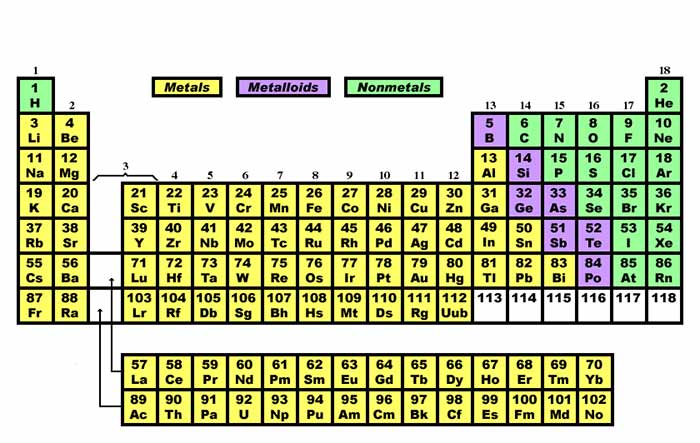
They form a separating boundary between the metals and nonmetals. Where is the right side. Boron B silicon Si germanium Ge arsenic As antimony Sb tellurium Te polonium Po and astatine At are the elements found along the step like line between metals and non-metals of the periodic table.
Block in the. 3 DIFFERENT TYPES OF ELEMENTS. Metals non-metals and metalloids.
Why is this information useful. Metalloids in a narrow. From left to right in the periodic table the nonmetals can be divided into the reactive nonmetals and the noble gases.
One useful way is by metals nonmetals and metalloids. Some elements between the metals and non-metals in the periodic table have properties which are a mixture of the properties of metals and non-metals. The periodic table is organized in families and periods.
Where are metals located on the periodic table Most metals are. In the periodic table you can see a zig-zag line starting at Boron B atomic number 5 and going all the way down to Polonium Po atomic number 84. The orange color on the Periodic table represents metalloids.
Also many periodic tables have a stair-step line on the table identifying the element groups. Elements are further classified into metals non-metals and metalloids based on their properties which are correlated with their placement in the periodic table. Atomic structure and the periodic table Elements in group 1 and group 2 are metals.
The noble gases are almost completely inert. SOLIDS LIQUIDS or GASSES What makes up most of the periodic table What is the classification of these characteristics. There are 118 elements known to us out of which 92 are naturally occurring while the rest have been prepared artificially.
Where at the metalloids located on the Periodic Table. Metals in most of the left and centre. Metals are found in the left side of the periodic table.
Metals are placed on the left side of the periodic table Non-metals are placed on the right side of the periodic table and Metalloids are placed in the middle of the periodic table. 9182015 24543 PM. Although they do not appear in the list of metalloid lists isolated.
Metals are located in s p d and f blocks in the periodic table though non-metals is located in s and p blocks and metalloids are located in p block of the periodic table. Elements of the periodic table are grouped as metals metalloids or semimetals and nonmetals. METALS NONMETALS METALLOIDS Classifying elements on the Periodic Table.
In other words metalloids semimetals are located on the right side of the post transition metals and on the left side of nonmetals see above image. Periodic table extract showing groups 12 and 1218 and a dividing line between metals and nonmetals. 1 This group of elements is made up of all different states of matter solid liquid and gas a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 2 These elements always have a shiny luster a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 3 These elements are located in a stair step pattern on the periodic table a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 4 Elements in this group are good conductors of heat AND.
An example of a metalloid is arsenic As. Periodic table separation of metals from nonmetals_Properties of metals metalloids and nonmetals WikipediaProperties of metals metalloids and nonmetals The periodic table showing. The line begins at boron B and extends down to polonium Po.
Summarize how the periodic table is organized in terms of metals nonmetals and metalloids. Difference Between Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Definition. Elements in the metalloids class fall in between the metals and nonmetals in their properties.
Arsenic is the element in opening photo B In the periodic table above elements are color coded to show their class. Where are the nonmetals located on the Periodic Table. Metals are elements having the highest degree of metallic behavior.
Percentages are median appearance frequencies in the list of metalloid lists. Metals are on the left of the periodic table and non-metals are on the right. Position in the Periodic Table.
Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids on the Periodic Table - YouTube A description and practice of finding metals nonmetals and metalloids on the Periodic TableIn general metals are found on the. The reactive nonmetals near the metalloids show some incipient metallic character such as the metallic appearance of graphite black phosphorus selenium and iodine. Nonmetals class generally cannot.
Atoms of group 1 elements have one. Sporadically recognised elements show that the metalloid net is sometimes cast very widely.
Oxygen nitrogen sulfur while most metals form cations eg. Most elements are metals.
Classification Of Elements In The Periodic Table Color Coding Yellow Download Scientific Diagram
Alkali metals and alkaline earth metals always form cations.

What elements are metals on the periodic table. The six alkaline earth metals are. Metals form ionic bonds with non-metals. These metals are considered to be both very rare and of high value.
Metals make up more than 70 percent of the Periodic Table of the Elements but many metals are unfamiliar to most of us. Remember thats the easy list. Eric Scerri 2007 The periodic table.
Alkaline Earth Metals The alkaline earth metals are found in column 2 on the left side of the Periodic Table. Most elements can be considered metals. They can be described as a lattice of positive ions surrounded by a cloud of delocalized electrons.
Subsequently one may also ask what percent of the elements on the periodic table are found in nature. The p-block elements together with the s-block elements the tall groups on the Periodic Table Electronegativity A measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons. Of those the two most rare metals are rhodium Rh and osmium Os.
This group includes alkali metals alkaline earth metals transition metals basic metals lanthanides rare earth elements and actinides. This list contains the 118 elements of chemistry. Chemical elements alphabetically listed The elements of the periodic table sorted by name in an alphabetical list.
Similarly one may ask what are the cations in the periodic table. Science Picture CoGetty Images. The reactivity increases as you move down the periodic table so cesium reacts explosively.
Periodic Table Metals A metal is an element that readily loses electrons to form positive ions cations and has metallic bonds between metal atoms. All of the elements in the alkali metal group are extremely reactive. Most elements can be considered metals.
Chemistry Metals and the Periodic Table of the Elements We use metals everyday. Lucky for you the periodic table is excellent at organizing elements and you will find each of these groups in specific areas of the periodic table. Most other nonmetals typically form anions eg.
Youll find metals like iron nickel chromium aluminum and cobalt in objects such as cookware cars and skyscrapers. The periodic table is organized in families and periods. Using the periodic table you can classify the elements in many ways.
If you put pure sodium or potassium metal in water the result will be a fire. This is a list of the 118 chemical elements which have been identified as of 2021. They are grouped together in the middle to the left-hand side of the periodic table.
Heres a quick list. A popular visualization of all 118 elements is the periodic table of the elements a convenient tabular arrangement of the elements by. Discovery of the Elements The Movie YouTube 118 The History Of Metals Timeline.
On the periodic table there is a family of eight elements known as the precious metals including elements 44 47 like silver and 76 79 like gold. Although separate on the periodic table lanthanides and actinides are really specific types of transition metals. The metals consist of the alkali metals alkaline earths transition metals lanthanides and actinides.
The periodic table also known as the periodic table of elements is organized so scientists can quickly discern the properties of individual elements such as their mass electron number electron configuration and their unique chemical properties. Metals In The Periodic Table So because most elements of the Table are metals it makes sense to begin by looking at them. Its story and its significance Oxford.
Actinide Metals Lanthanide Metals Alkali Metals Alkaline-Earth Metals Rare Metals Rare-Earth Metals and Transition Metals. One useful way is by metals nonmetals and metalloids. Click on any elements name for further chemical properties environmental data or health effects.
A timeline showing the discovery of metals and the development of metallurgy. They are generally harder and denser than alkali metals have 2 electrons in their outermost s sub-shell and each make a distinct color in their flames. Halogens always form anions.
They are grouped together in the middle to the left-hand side of the periodic table. The metals consist of the alkali metals alkaline earths transition metals lanthanides and actinides. The pure element would like explode on contact with skin.
Metals reside on the left side of the table while non-metals reside on the right. History of Elements of the Periodic Table. Timeline of Element Discoveries.
Metals In the periodic table you can see a stair-stepped line starting at Boron B atomic number 5 and going all the way down to. A chemical element often simply called an element is a species of atoms which all have the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei ie the same atomic number or Z. The metals are one of the three groups of elements as.
If you look at the Periodic table you will find that the metal elements are located between atomic number 5 Boron B all the way to atomic number 84 Polonium Po.
Alkaline Earth Metals The alkaline earth metals are found in column 2 on the left side of the Periodic Table. From above image you can easily find where Inner Transition Metals are located on Periodic Table.
The alkaline earth metals represent the second column on the periodic table.
Where are the metals located on the periodic table. Atomic number 32 Germanium Ge. A description and practice of finding metals nonmetals and metalloids on the Periodic TableIn general metals are found on the left-hand side of the period. Its monatomic form H is the most abundant chemical substance in the Universe constituting roughly 75 of all baryonic mass.
Its six elements extend from beryllium Be to radium Ra. If you look at the Periodic table you will find that the metal elements are located between atomic number 5 Boron B all the way to atomic number 84 Polonium Po. The six alkaline earth metals are.
Metalloids or Semimetals There is a zig-zag line toward the right side of the periodic table that acts as a sort of border between metals and nonmetals. And atomic number 52 Antinomy Sb. Most periodic tables print a thick black line to show the division between metals and nonmetals.
Except for Germanium Ge and Antimony Sb all the elements to the left of that line can be classified as metals. There are multiple ways of grouping the elements but they are commonly divided into metals semimetals metalloids and nonmetals. These elements are located below the table because there wasnt a practical way to insert them into the transition metal section without making the table look strange.
This is what is meant by periodicity or periodic table trends. Inner transition metals are located in the two rows at the bottom of the periodic table. The elements on the left of the periodic table are metals.
In the periodic table you can see a stair-stepped line starting at Boron B atomic number 5 and going all the way down to Polonium Po atomic number 84. Silicon one row down in the same family is a true metalloid. Atoms to the left of the.
Alkaline earth metals are located just next to the alkali metals. The outer shell of a metal is therefore less than half full of. Alkaline earth metals includes.
This line is often referred to as the staircase because of its shape. This above image shows you where are alkaline earth metals found on the Periodic table. These metals are named for forming basic solutions when put into water.
These metals will have 1 2 or 3 electrons in the outer shell. With a standard atomic weight of circa 1008 hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table. There is no scientific reason for this.
In other words the transition of metallic nature to nonmetallic nature appears in these elements. Depending on conditions elements belonging to the metalloid group may behave like metals. These two rows at the bottom of the Periodic table are called.
There are only two exceptions ie two elements in that sequence between number 5 and number 84 that are not metals. Carbon is a non metal but has some metallic properties. These rows contain elements in the lanthanoid and actinoid series usually from 57 to 71 lanthanum to lutetium and 89 to 103 actinium to lawrencium respectively.
Lanthanides Ce Lu having atomic number from 58 71 and. The periodic table shows that metals are found in groups 1 2 and 3. They are generally harder and denser than alkali metals have 2 electrons in their outermost s sub-shell and each make a distinct color in their flames.
In general metals are located on the left-hand side of the periodic table decreasing in metallic character moving up and to the right. And transition metals form a bridge between them. Periodic table of the elements materials science and academic information elements and advanced materials data scientific presentations and all pages designs concepts logos and color schemes herein are the copyrighted proprietary rights and intellectual property of American Elements.
Hydrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 1 which means there are 1 protons and 1 electrons in the atomic structureThe chemical symbol for Hydrogen is H. The creator of the periodic table Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869 began collecting and sorting known properties of elements like he was playing a game while traveling by train. Beryllium Be Magnesium Mg Calcium Ca Strontium Sr Barium Ba and Radium Ra.
Seeing chemical elements arranged in the modern periodic table is as familiar as seeing a map of the world but it was not always so obvious. They tend to form cations with a positive two charge and bond ionically. Alkaline earth metals are found in the 2nd group of the Periodic table.
In addition even nonmetals may be metals. The periodic table has two rows at the bottom that are usually split out from the main body of the table. Metals are on the left side of periodic table and nonmetals are on the right side of periodic table.
Electron negativity decreases as the size of the element increases in a family. One reason the periodic table of the elements is so useful is that it is a means of arranging elements according to their similar properties.
What is Carbon. Their shape can be easily changed into thin wires or sheets without breaking.
Matter And Energy Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids Texas Gateway
Nonmetals are elements showing less or no metallic properties.

Metals nonmetals and metalloids on periodic table. Can a metalloid have properties of metals and nonmetals. Most elements are metals. Properties of Metalloids Metalloids are malleable and ductile Families Families in the periodic table share chemical properties because all elements in a family have the same number of valence electrons This means that all elements in a.
1 This group of elements is made up of all different states of matter solid liquid and gas a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 2 These elements always have a shiny luster a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 3 These elements are located in a stair step pattern on the periodic table a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 4 Elements in this group are good conductors of heat AND electricity a Nonmetals b Metals c Metalloids 5 This tells you. Where at the metalloids located on the Periodic Table. Metalloids tend to be economically important because of their unique conductivity properties they only partially conduct electricity which make them valuable in the semiconductor and computer chip industry.
The line begins at boron B and extends down to polonium Po. An Introduction to General Organic and Biological Chemistry 12th. Metalloids Some elements between the metals and non-metals in the periodic table have properties which are a mixture of the properties of metals and non-metals.
Metals are placed on the left side of the periodic table Non-metals are placed on the right side of the periodic table. Where are metals located on the periodic table Most metals are. Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids on the Periodic Table - YouTube A description and practice of finding metals nonmetals and metalloids on the Periodic TableIn general metals are found on the.
Metals are found in the left side of the periodic table. The metalloids have some of the characteristics of metals and some of the characteristics of nonmetals. Metals are elements having the highest degree of metallic behavior.
The most common metalloid is silicon Si. The orange color on the Periodic table represents metalloids. The metals are to the left of the line except for hydrogen which is a nonmetal the nonmetals are to the right of the line and the elements immediately adjacent to the line are the metalloids.
On many periodic tables a jagged black line see figure below along the right side of the table separates the metals from the nonmetals. In other words metalloids semimetals are located on the right side of the post transition metals and on the left side of nonmetals see above image. The noble gases are almost completely inert.
Position in the Periodic Table. SOLIDS LIQUIDS or GASSES What makes up most of the periodic table What is the classification of these characteristics. The metalloids separate the metals and nonmetals on a periodic table.
Learn about the metals nonmetals and metalloids and the periodic table. The reactive nonmetals near the metalloids show some incipient metallic character such as the metallic appearance of graphite black phosphorus selenium and iodine. Metals are at the left nonmetals are at the right and metalloids straddle a zig-zag line that separates metals from nonmetals.
The seven metalloids are boron silicon germanium arsenic antimony tellurium and polonium. Also many periodic tables have a stair-step line on the table identifying the element groups. The metals green in the table nonmetals orange and metalloids blue.
Difference Between Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Definition. Properties of Metalloids They conduct electricity and heat better than nonmetals but not as well as metals. The Metalloids On the border between the metals and the nonmetals are seven elements called metalloids.
They are usually shiny very dense and only melt at high temperatures. These elements are called metalloids. Development of the Periodic table Effective Nuclear Charge Atomic and Ionic sizes.
Metalloids are elements having a low degree of metallic behavior. They form a separating boundary between the metals and nonmetals. Metals are located in s p d and f blocks non-metals are located in s and p blocks whereas metalloids are located in p blocks of the periodic table Metals have high thermal and electrical conductivity while non-metals tend to be low and metalloids are good conductors.
Key Differences Between Metals Non-Metals and Metalloids Metals are the elements which exhibit the highest degree of metallic behavior is known as metals on the contrary. The periodic table on the left separates elements into three groups. The metalloids or semimetals have properties that are somewhat of a cross between metals and nonmetals.
The metals are found on the left and the nonmetals are found on the right. Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Chemistry 101 Periodic Table properties. Elements of the periodic table are grouped as metals metalloids or semimetals and nonmetals.
Metals Nonmetals Metalloids - Maze chase. The three types of elements occupy their own places in the Periodic Table. From left to right in the periodic table the nonmetals can be divided into the reactive nonmetals and the noble gases.
Metalloids are located between the metals and nonmetals.